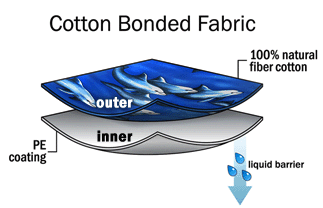
Bonded fabric,
A lightweight, usually knitted, cloth which is strengthened and thickened by having a lining material fixed to it permanently by means of heat and pressure. Often a very thin layer of foam interlining is placed between two layers of the fabric.
A lightweight, usually knitted, cloth which is strengthened and thickened by having a lining material fixed to it permanently by means of heat and pressure. Often a very thin layer of foam interlining is placed between two layers of the fabric.
Bone Folder,
Bone Folder refers to a knife like instrument made from bone, which is used to form a smooth crease when folding a sheet of paper.
Bone Folder refers to a knife like instrument made from bone, which is used to form a smooth crease when folding a sheet of paper.
Bora,
Waistband of tiny silver beads that resemble smallpox postules and are meant to ward off the disease.
Waistband of tiny silver beads that resemble smallpox postules and are meant to ward off the disease.
Boria,
A style of embroidery, primarily consisting of pako embroidery with scattered white single chain stitches, used by Haliputra women in Kutch, Gujarat.
A style of embroidery, primarily consisting of pako embroidery with scattered white single chain stitches, used by Haliputra women in Kutch, Gujarat.
Bostani,
A square embroidered kantha used to wrap valuables when trunks and suitcases were not available. Possibily is a deriative from the local word ‘bosta’ or bundle.
A square embroidered kantha used to wrap valuables when trunks and suitcases were not available. Possibily is a deriative from the local word ‘bosta’ or bundle.
Boundage,
The term used in late Georgian times (when dark printed grounds were in fashion) for the thick edge the block cutter left to his outlines to make the fitting of the background block easier.
The term used in late Georgian times (when dark printed grounds were in fashion) for the thick edge the block cutter left to his outlines to make the fitting of the background block easier.
Bow,
An instrument, usually made be bent bamboo and held taut with twine stretched between each end, used to fluff cotton fibre during the carding process. The string of the bow is struck to produce vibrations which loosen any packed cotton fibres.
An instrument, usually made be bent bamboo and held taut with twine stretched between each end, used to fluff cotton fibre during the carding process. The string of the bow is struck to produce vibrations which loosen any packed cotton fibres.
Braid,
A general term to describe a flat, decorative, woven or plaited tape or band used particularly to trim border.
A general term to describe a flat, decorative, woven or plaited tape or band used particularly to trim border.
Braid weaving,
The process of producing narrow bands of braid. Some types of braid are woven on narrow looms, while other braid is produced by interlacing elements by plaiting or twining.
The process of producing narrow bands of braid. Some types of braid are woven on narrow looms, while other braid is produced by interlacing elements by plaiting or twining.
Brake,
A device to hold a warp beam from turning, made of a metal cable or band which winds on a metal drum.
A device to hold a warp beam from turning, made of a metal cable or band which winds on a metal drum.
Brass,
An alloy of copper and zinc. It used to be made by melting copper in contact with the zinc carbonate, calamine (ZnCO3), under charcoal in a crucible. Early brasses contained 70-90% copper and 10-30% zinc. The colour of brass changes with increasing zinc content from a rich copper-red through to pale yellow to white as the zinc increases. Gilding metal containing 10-15% zinc is suitable for cold working. It is used for ornamental work and jewellery. Red brass contains 30% zinc and 70% copper and has good working properties. The common form of brass is 60% copper, 40% zinc and is known as yellow brass or Muntz metal. In Europe from about 1750 it was made by melting the two metals together (Direct process).
An alloy of copper and zinc. It used to be made by melting copper in contact with the zinc carbonate, calamine (ZnCO3), under charcoal in a crucible. Early brasses contained 70-90% copper and 10-30% zinc. The colour of brass changes with increasing zinc content from a rich copper-red through to pale yellow to white as the zinc increases. Gilding metal containing 10-15% zinc is suitable for cold working. It is used for ornamental work and jewellery. Red brass contains 30% zinc and 70% copper and has good working properties. The common form of brass is 60% copper, 40% zinc and is known as yellow brass or Muntz metal. In Europe from about 1750 it was made by melting the two metals together (Direct process).
Breast-beam,
The beam in the backstrap tension loom closest to the weaver, around which the woven section of the warp moves or is rolled. It is also known as the cloth-beam. The backstrap of the loom is attached to this beam. Beam at the front of the loom over which the cloth passes before it winds onto the cloth beam
The beam in the backstrap tension loom closest to the weaver, around which the woven section of the warp moves or is rolled. It is also known as the cloth-beam. The backstrap of the loom is attached to this beam. Beam at the front of the loom over which the cloth passes before it winds onto the cloth beam
Brocade,
A general term referring to the patterning of woven fabric by means of supplementary threads. It is usually applied to silk fabric richly patterned with gold or silver weft thread.
A general term referring to the patterning of woven fabric by means of supplementary threads. It is usually applied to silk fabric richly patterned with gold or silver weft thread.
Bronze,
In antiquity and historical usage, an alloy of copper and tin. Usually with up to 14% tin, but many examples of ancient alloys are known with higher tin contents. 14% tin is the limit of solid solution of tin in well annealed alpha-bronzes. In modern usage, the term bronze is associated with a number of copper alloys that may contain no tin at all and in which case the composition of the alloy should be specified.
In antiquity and historical usage, an alloy of copper and tin. Usually with up to 14% tin, but many examples of ancient alloys are known with higher tin contents. 14% tin is the limit of solid solution of tin in well annealed alpha-bronzes. In modern usage, the term bronze is associated with a number of copper alloys that may contain no tin at all and in which case the composition of the alloy should be specified.
Bronze,
Mixture of copper, tin, and other metals often used in cast sculptures because it is very strong and hard.
Mixture of copper, tin, and other metals often used in cast sculptures because it is very strong and hard.